Abbreviations:
ISDN-Integrated Services Digital Network
CCIT-Consultative Committee on International Telegraph and Telephone
PTT-Post Telegraph and Telephone
ITU-International Telecommunication Union
TSS-Telecommunications Standard Subsection
BRI-Basic Rate Interface
TDM-Time−Division Multiplexed
HDLC-high−level data link control
TE1-terminal equipment type 1
TE2-terminal equipment type 2
TA-Terminal Adapter
SOHOs-Small Offices or home offices
PRI-Primary Rate Interface
History
A long time ago, the entire telephone network was analog. And that time, as a voice went farther down the line, and through more switches, the quality became worse and worse as noise crept in. And there was no way to eliminate the noise.With the transistor revolution, this theory became possible, and the phone companies began converting their own networks over to digital.Thus, IDSN was created.
What is ISDN?
The Basics
ISDN is based on a number of fundamental building blocks. First, there are two types of ISDN "channels" or communication paths:
B-channel
The Bearer ("B") channel is a 64 kbps channel which can be used for voice, video, data, or multimedia calls. B-channels can be aggregated together for even higher bandwidth applications
D-channel
The Delta ("D") channel can be either a 16 kbps or 64 kbps channel used primarily for communications (or "signaling") between switching equipment in the ISDN network and the ISDN equipment at your site.
Two pre-defined configurations
Basic Rate Interface (BRI)
BRI is the ISDN service most people use to connect to the Internet. An ISDN BRI connection supports two 64 kbps B-channels and one 16 kbps D-channel over a standard phone line.
Primary Rate Interface (PRI)
SDN PRI service is used primarily by large organizations with intensive communications needs. An ISDN PRI connection supports 23 64 kbps B-channels and one 64 kbps D-channel (or 23B+D) over a high speed DS1 (or T-1) circuit.
Origins of the Standards
The CCITT is a consultative committee to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and have recently changed their name to ITU−T.The ITU−T (CCITT) is a UN treaty organization and, as such, each country is entitled to send representatives to any committee meeting.The name ITU−T came about due to the privatization trend separating telephone business from the post office and the general elimination of telegraph service.
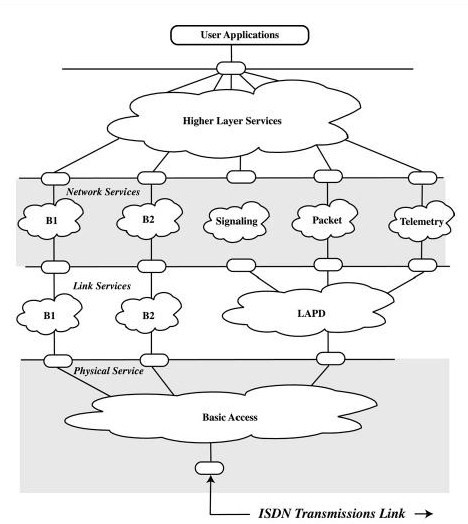
Architecture of the ISDN interface
Interface Components
A. NT1 - It creates the T interface for premise devices (from the U interface).
B. NT2 - This device would do the switching, permitting more than the standard eight devices to share the bus by creating perhaps multiple S buses.
C. TE1 - is a standard ISDN terminal that is capable of dealing with the B and D channels. In other words,it can interface with the S/T bus.
D. TE2 - is a standard device having an RS−232 or V.35 interface.
E. TA - is the semi−intelligent device that lets a TE2 connect to the S/T ISDN interface.
Typical local loop layout
The U Interface
The Physical Interface
Applications of the ISDN Interface
Multiple Channels
The plan is to provide access to every possible home device. The original concept was for up to eight devices. After all, you only have two B channels and one D channel to share among eight devices.
Telephone
Instead of the telephone conversation being analog from the handset to the central office where it becomes digitized, the conversation can be digitized directly at the source and passed digitally all the way through the network to the other end.
Digital Fax
Fax machines now have to be digital. Therefore, the Group IV fax standard specifies 64 KBps fax operation.
Analog Fax
Analog fax machines use a modem, so it has to plug into the telephone that would take the analog modem tones and digitize them at 64 KBps. This would provide compatibility with all existing Group III fax machines.
Computer/Video Conferencing
Our computer or video conferencing equipment can use one of the 64 KBps or bond both bearerchannels together for a 128 KBps digital channel across the network.
Signaling
The primary function of the data channel is to provide for signaling, that is, the setting up and tearing down of the switched bearer channels.
Telemetry
The concept is that many household devices can be connected to the data channel.The concept also includes connecting the utility meters to permit remote monitoring and billing.
Packet Switching
The 16 KBps data channel has bandwidth to spare. Therefore, the local carrier can provide a data
service on this excess bandwidth.
Broadband ISDN
B-ISDN is designed to handle high-bandwidth applications. BISDN currently uses ATM technology over SONET-based transmission circuits to provide data rates from 155 to 622Mbps and beyond, contrast with the traditional narrowband ISDN (or N-ISDN), which is only 64 Kb ps basically and up to 2 Mbps.
Why Should I Use ISDN to Access the Internet?
More and more people are discovering that ISDN is the right Internet answer. As the Internet becomes more and more information-intensive with graphics, sound, video and multimedia, your ability to take advantage of these new resources depends on the speed of your Internet connection
With ISDN, your Internet access is:
Even faster
By combining your two B-channels you have access to up to 128 kbps -- more than four times as fast as a 28.8 kbps modem on a standard phone line. And ISDN's digital technology assures you the cleanest connection to the Internet so you won't be slowed down by re-transmissions because of old analog technology.
More efficient and economical
ISDN brings increased capabilities, reduced costs and improved productivity to organizations both large and small. When you're looking for something on the Internet, you can get there faster. You can be more productive because you aren't waiting as long to get to that next website or download that large file.
ISDN brings increased capabilities, reduced costs and improved productivity to organizations both large and small. When you're looking for something on the Internet, you can get there faster. You can be more productive because you aren't waiting as long to get to that next website or download that large file.
http://public.swbell.net/ISDN/overview.html
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3dU7pSQ_D1M
Broadband Telecommunications Handbook (VPN 3GW GPRS MPLS VoIP SIP).pdf




its nice to read a useful article for beginner like me. Some of points from this article are very helpful for me as I haven’t considered them yet. I would like to say thank you for sharing this cool article. Bookmarked and sharing for friends
TumugonBurahinInfiniti G35 AC Compressor
nice pagka post sa imng blog kay klaro siya pag ka summary sa chapter 10....
TumugonBurahinThe topic gives me learning and broad knowledge of what the ISDN is for....thank you
TumugonBurahinoh well, very informative..Thanks for sharing this thing.
TumugonBurahinISDN was a good and interesting technology.it is overwhelming to know that a lot were exerting effort to spread such information.
TumugonBurahinis there any upgrades about the isdn?
TumugonBurahinISDN IS A GOOD WAY OF NETWORKING... Thanks for sharing this article. Nice article very informative..
TumugonBurahinI agree about the ISDN being efficient. but i doubt that it is more economical. based on my other searches, ISDN is more expensive to install and also its rent is more expensive. another is, it requires an engineer to install the ISDN. please clarify. it would be very much appreciated. thanks! :D Nice Post though. Very informative. thanks again.
TumugonBurahinis there any advantages and disadvantages does the ISDN have.?
TumugonBurahinhttp://www.fim.uni-linz.ac.at/research/telework/seminar/T2/isdn.html you can click this page to see the advantage and disadvantage of an ISDN :P
BurahinThe applications of the ISDN Interface was very much appreciated by the present generation...
TumugonBurahinwhat a informative post... TY nivla
keep it up ;)
Your welcome sister... hihih.. and also your blog was astonishing..very wonderful indeed..
BurahinIs there any disadavantage of using ISDN?
TumugonBurahinhello vin.. can you discuss How Does ISDN work.?. coz my mind is buffering..,i still dont get d point..
TumugonBurahinis ISDN still being used nowadays? wat do you prefer to use DSL or IDSN? and why?
TumugonBurahin