As the convergence of wireless technology and the Internet continue at an escalating pace, the new possibilities created by 3G and 4G technologies appear endless. Preparing for the revolution, existing Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) operators must evolve their networks to take advantage of Mobile Multimedia applications and the eventual shift to an all−IP architecture. One way to do that is through the evolution of General Packet Radio Services (GPRS). However, soon after we see the installation of GPRS, some operators will begin the next step in the evolution process to Enhanced Data for Global Environment (EDGE).
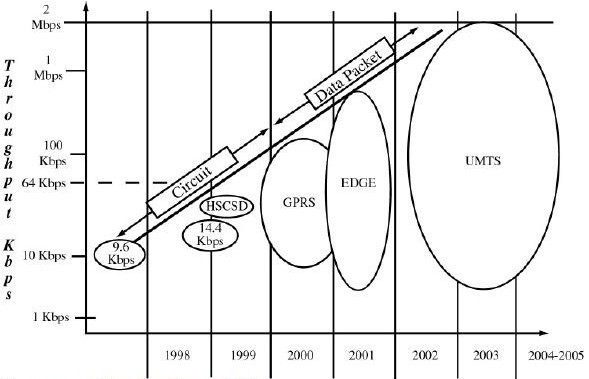
Probably the most important aspects of GPRS are that it enables data transmission speeds up to 170 Kbps, it is packet based, and it supports the leading data communications protocols (IP and X. 25). GPRS operates at much higher speeds than current networks, providing advantages from a software perspective. Wireless middleware currently is required to enable slow speed mobile clients to work with fast networks for applications such as e−mail, databases, groupware, or Internet access. With GPRS, wireless middleware will probably be unnecessary, making it easier to deploy wireless solutions.
EDGE, Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution, is a further step for GSM to migrate to 3G. It uses a new air-interface technology -- 8 Phase Shift Keying Modulation (8-PSK) to offer 48 kbits/s per GSM timeslot. The overall offered data speeds of 384Kbps places EDGE as an early pre-taste of 3G and it is actually labeled as 2.75G by the industry.
EDGE is occasionally referred to as Enhanced GPRS (EGPRS) because it increases the capacity and data throughput of GPRS by three to four times. Like GPRS, EDGE is a packet-based service, which provides customers with a constant data connection.
For EDGE to be effective it should be installed along with the packet-switching upgrades used for GPRS. This entails the addition of two types of nodes to the network: the gateway GPRS service node (GGSN) and the serving GPRS service node (SGSN). The GGSN connects to packet-switched networks such as internet protocol (IP) and X.25, along with other GPRS networks, while the SGSN provides the packet-switched link to mobile stations.
By providing an upgrade route for GSM/GPRS and TDMA networks, EDGE forms part of the evolution to IMT-2000 systems. Since GPRS is already being deployed, and IMT-2000 is not expected until 2002, there is a definite window of opportunity for EDGE systems to fill in as a stop-gap measure.
EDGE Network Architecture
UMTS
Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) is one of the third-generation (3G) cell phone technologies. Currently, the most common form of UMTS uses W-CDMA as the underlying air interface. It is standardized by the 3GPP, and is the European answer to the ITU IMT-2000 requirements for 3G cellular radio systems.
UMTS is packet-based and it allows transmission of text, digitized voice, video, and multimedia at data rates up to 2 megabits per second (Mbps). UMTS offers a consistent set of services to mobile computer and phone users, no matter where they are located in the world.
EDGE Network Architecture

A UMTS network consists of three domains; Core Network (CN), UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN) and User Equipment (UE). The main function of the core network is to provide switching, routing and transit for user traffic. Core network also contains the databases and network management functions.
The basic Core Network architecture for UMTS is based on GSM network with GPRS. All equipment has to be modified for UMTS operation and services. The UTRAN provides the air interface access method for User Equipment. Base Station is referred as Node-B and control equipment for Node-B's is called Radio Network Controller (RNC).
Broadband Telecommunications Handbook (VPN 3GW GPRS MPLS VoIP SIP).pdf







The 3G has the speed that the user wanted and is the latest that has been wide spread to the world today. 3G is the most common use of the people today. Good Job ^_^
TumugonBurahinone of the most important aspects of 3G wireless technology is its ability to unify existing cellular standards...
TumugonBurahinnice blog pal..keep it up ;)
3G networks use a variety of wireless network technologies, including GSM, CDMA, TDMA, WCDMA, CDMA2000, UMTS and EDGE, and this leads to some confusion as well as a great deal of flexibility.
TumugonBurahin3G had to deliver packet-switched data with better spectral efficiency, at far greater speeds.
TumugonBurahinHowever, to get from 2G to 3G, mobile operators had make "evolutionary" upgrades to existing networks while simultaneously planning their "revolutionary" new mobile broadband networks.
EDGE is occasionally referred to as Enhanced GPRS (EGPRS) because it increases the capacity and data throughput of GPRS by three to four times. Like GPRS, EDGE is a packet-based service, which provides customers with a constant data connection.
TumugonBurahinThank You for the information Alvin..
Well Done..